testing the hardness of metals|metal hardness testing near me : dealers Today, hardness testing is one of the most widely used methods in mechanical materials testing, especially for metals. On the one hand, this test method can be used to find qualitative relations to other material properties (e.g., strength, . The area. Rua Cipriano Barata 1364 Ipiranga, Sao Paulo, State of Sao Paulo 04205-001 Brazil. Neighbourhood: Ipiranga. Named after the Ipiranga River, this region is home to .
{plog:ftitle_list}
webOutra forma de obter uma segunda via da fatura Click Telecom é através da central de atendimento da empresa. Para isso, siga o seguinte passo a passo: Ligue para o telefone: 0800 380 0800; Informe o CPF ou CNPJ do titular da conta; Solicite junto ao atendente, uma segunda via do seu boleto; A nova via será enviada para o e-mail cadastrado .
The most common methods used for testing the hardness of metals are Rockwell, Brinell, Vickers, and Knoop. Each of these methods employs different indenters and loads to measure the material’s resistance to plastic .
Today, hardness testing is one of the most widely used methods in mechanical materials testing, especially for metals. On the one hand, this test method can be used to find qualitative relations to other material properties (e.g., strength, .
Materials are tested using various methods, with each test expressing hardness using its own arbitrarily defined scale. In this article we shall explore five of the most common test methods for measuring the hardness of .There are several frequently used methods to measure the hardness of metals, including: 1 Rockwell Hardness. The Rockwell hardness test measures the depth of penetra-tion of an . Today, hardness testing is among the most commonly used methods in mechanical materials testing, particularly for metals. This testing method can be applied to determine qualitative relations to other material . The Brinell hardness scale is a widely accepted measure of hardness in materials. It involves pressing a ball of steel (or tungsten carbide for harder materials) into the test piece at a constant and known force. The softer .
steel hardness testing methods
A Vickers hardness tester. The Vickers hardness test was developed in 1921 by Robert L. Smith and George E. Sandland at Vickers Ltd as an alternative to the Brinell method to measure the hardness of materials. [1] The Vickers test is often easier to use than other hardness tests since the required calculations are independent of the size of the indenter, and the indenter .
The Brinell hardness testing method is used in various cases where large or rough surfaces, coarse-grained materials, or high loads are involved. It is particularly well-suited for testing the hardness of materials with relatively low hardness ranges, such as non-ferrous metals, castings, and softer steels. Related reading: Metal Hardness Comparison Chart: HV, HB, HRC Commonly Used Hardness Brinell Hardness. The Brinell hardness test uses a ball made of hardened steel or a hard alloy with a diameter of D as the .
Brinell hardness. The Brinell hardness scale is a widely accepted measure of hardness in materials. It involves pressing a ball of steel (or tungsten carbide for harder materials) into the test piece at a constant and known force. The softer the material, the deeper the ball will penetrate and vice versa. The next step is to take a measurement of the diameter . A numerical hardness value is assigned to the test material based on the results of the test. Mohs hardness test uses 10 reference materials of varying hardness as the scale for the test. The softest material used is talc (value=1) and .
sheet metal hardness chart
The Vickers hardness test method was developed by Robert L. Smith and George E. Sandland at Vickers Ltd as an alternative to the Brinell method to measure the hardness of materials. The Vickers hardness test method can be also used as a microhardness test method, which is mostly used for small parts, thin sections, or case depth work. Since the .
Hardness testing standards have been set by various organisations such as The American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) and The International Organisation for Standardisation (ISO), prescribing specific varieties of a hardness test determined by factors such as the type of indenter, applied force, and procedure of force application.The Vickers hardness test is often regarded as easier to use than other hardness tests: The process can be performed on a universal or micro hardness tester; the required calculations are independent of the size of the indenter; and the same indenter (a pyramidal diamond) can be used for all materials, irrespective of hardness. Rebound hardness testing is primarily used for metal materials. The method involves using a special small hammer that is dropped from a specific height to impact the material sample being tested. The material’s hardness is determined by the amount of strain energy stored in and then released from the sample during the impact, which is .The typical test uses a 10 mm (0.39 in) diameter steel ball as an indenter with a 3,000 kgf (29.42 kN; 6,614 lbf) force.For softer materials, a smaller force is used; for harder materials, a tungsten carbide ball is substituted for the steel ball. The indentation is .
metals ranked by hardness
The Vickers hardness test method was developed by Robert L. Smith and George E. Sandland at Vickers Ltd as an alternative to the Brinell method to measure the hardness of materials. The Vickers hardness test method can be also used as a microhardness test method, which is mostly used for small parts, thin sections, or case depth work. Since the . The Brinell hardness test is ideal for measuring the hardness of metals with coarse or inhomogeneous grain structures, such as cast iron and softer metals like aluminum alloys. It measures the diameter of a larger indentation, which averages out variations in the material’s microstructure, providing a more representative hardness value for .
Hardness testing assesses the impact of the metal or alloy to permanent indentation, and the depth or size of the indent is measured to determine a hardness value. There are several different hardness tests and we use the Brinell, Vickers and Rockwell methods.Hardness testing on metals is used to evaluate the resistance of a metal to deformation or permanent damage, specifically in terms of indentations or scratching. It involves applying a consistent force using a rounded or pointed object under controlled conditions to create a small dent on the surface of a metal. The size of the dent is then .
In the Rockwell hardness test, a differential-depth method, the residual depth of the indent made by the indenter, is measured.In contrast, the size of the indentation is measured in the Brinell, Vickers and Knoop optical test .
E10-23 Standard Test Method for Brinell Hardness of Metallic Materials . E92-23 Standard Test Methods for Vickers Hardness and Knoop Hardness of Metallic Materials . E2546-15(2023) Standard Practice for Instrumented Indentation Testing . E18-24 Standard Test Methods for Rockwell Hardness of Metallic Materials . E103-24 Standard Practice for . The test specimens have been standardized by ASTM (American Society of Testing Materials). Engineering Stress Strain Relationship. . What are the advantages and disadvantages of the Brinell hardness test? .When testing for hardness, remember that you are testing "the resistance to scratching." During the test, some materials might fail in other ways. They could break, deform, or crumble instead of scratching. Hard materials often break when subjected to stress. This is a lack of toughness. Other materials might deform or crumble when subjected to .The Rockwell test is generally easier to perform, and more accurate than other types of hardness testing methods. The Rockwell test method is used on all metals, except in condition where the test metal structure or surface conditions would introduce too much variations; where the indentations would be too large for the application; or where .

The depth of the indenter is 0.01mm, which uses the Wechsler hardness unit (referenced as HW). The full range has only 20 graduations so a typical instrument is limited when testing metallic materials. 7. Leeb Hardness Testers. The Leeb hardness testing method, also known as the Equotip method, was first invented by a swiss company in 1975.ACKNOWLEDGMENTS Theauthorwouldliketothankthefollowingpersonsforsharingtheir experienceandprovidinginformationforthisGuide.Theirinputandreview . Materials that fall into a very high hardness scale or thin and small components tend to be better suited for Knoop or Vickers testing. Vickers methods are widely used for microhardness testing, which is essential for measuring the hardness of small or thin materials or for analyzing the hardness of specific microstructures in a material. This . Heat treating has evolved into a highly complex, precise process that improves characteristics of metal parts. A critical component of quality heat treating is employing the correct hardness testing method to show manufacturers their parts achieve design requirements.
metal hardness testing near me
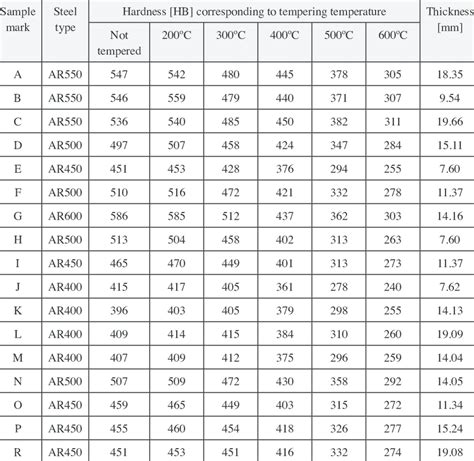
There are two principal methods of testing the hardness of a material – scratch testing and indentation testing. Indentation testing can only be used on materials that undergo plastic deformation such as metals and thermoplastic polymers. Scratch testing is therefore used for brittle materials such as ceramics. Scratch testingIn the Brinell Hardness Testing, the hardness of a metal is determined by measuring the permanent indentation size produced by an indenter. Harder materials will generate shallow indentations while softer materials will produce deeper indentations. This test method was first proposed by Swedish engineer Johan August Brinell in 1900 and .
Nonmetals are often softer than metals, particularly transition metals. While diamond is pure carbon and is a nonmetal, other carbon allotropes are softer. Perform the Mohs Hardness Test. The Mohs hardness test is easily performed. You need examples of items with known hardness values. Handy materials include: your fingernails (2.5)
Pros: Good for testing materials with coarse or uneven grain structures. Cons: Not suitable for very hard or thin materials. Industrial Use: Widely used in the metal industry, particularly for softer metals. Vickers Hardness Test. Uses a diamond pyramid indenter pressed into the material. The size of the indentation determines the hardness.
metal hardness testing methods
how to test steel hardness
Jordana. Download Full Pack. pixeldrain.com. Salve. Segue conteúdo inédito. 6 files. pixeldrain.com. até o pai dela já viu esse conteudo dela ai. Foi por causa desses .
testing the hardness of metals|metal hardness testing near me